EF Core architecture
EF Core architecture
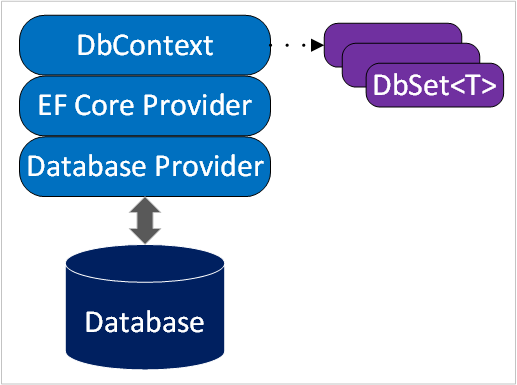
Classes deriving from DbContext:
DbContext:The EF Core Provider translates object graph changes to SQL.
The Database Provider:
Last updated